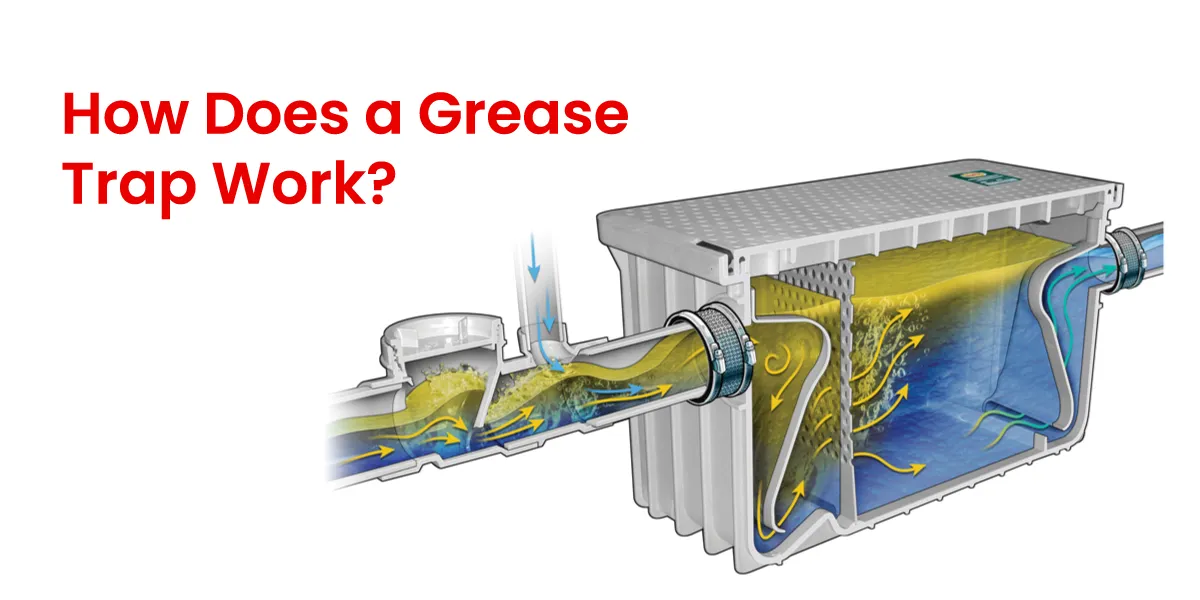
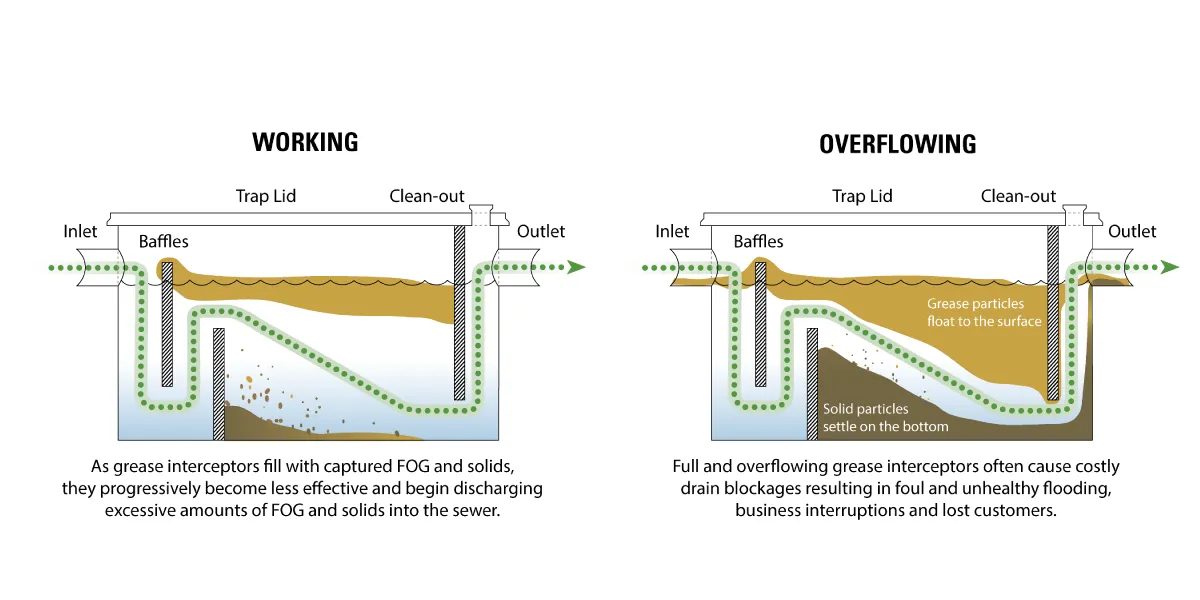
Plastic pollution is a serious problem for the globe today, which has prompted academics and business leaders to look for sustainable alternatives. Making bioplastics out of used oil, which is frequently regarded as waste, is one possible approach. This procedure helps create biodegradable polymers that can take the place of conventional petroleum-based plastics in addition to addressing the disposal problems related to spent oil.
Processes Involved in Conversion
There are multiple phases involved in turning spent oil into bioplastics, beginning with collection and purification. To start, the oil needs to be filtered to get rid of pollutants and food particles.
After purification, the cleaned oil is usually subjected to a catalytic process, which breaks down the long-chain hydrocarbons in the oil through chemical reactions. In this stage, catalysts are essential because they help transform these hydrocarbons into more manageable monomers that can then be polymerized into bioplastics.
Upon production, the monomers can be polymerized using different techniques including addition or condensation polymerization, based on the desired characteristics of the final bioplastic product. The resulting bioplastics’ mechanical and thermal characteristics will vary depending on the type of polymerization process employed, which will suit various uses.
Potential Applications of Bioplastics
Numerous applications exist for the bioplastics made from spent oil. These consist of disposable cutlery, packaging supplies, and even parts for the building and automobile sectors. Bioplastics are a desirable substitute for traditional plastics due to their adaptability, particularly in sectors looking to lessen their environmental impact.
The Conversion Process
Utilizing cutting-edge technologies, there are multiple essential phases involved in turning spent oil into bioplastics. To start with, the waste oil is purified to get rid of impurities and make sure it is clean. Following refinement, refined oil is put through chemical reactions such pyrolysis or transesterification to create monomers that can be used in polymerization.
Environmental Benefits
Making use of used oil has major environmental benefits. We lessen the amount of waste that would otherwise clog landfills and contaminate the environment by recycling spent oil. Because the method uses a renewable resource, it also lessens our dependency on fossil fuels for the production of plastic. By being biodegradable, the resultant bioplastics can reduce their ecological impact even more.
Applications of Bioplastics
One of the most attractive aspects of bioplastics made from spent oil is their adaptability. Applications for these materials are numerous and include consumer items, construction materials, automobile parts, and packaging. For example, bioplastics can take the role of conventional plastic in single-use products like bags and containers, which are big polluters of the environment.
Moreover, bioplastics derived from spent oil can be utilized for interior car parts, which helps make cars lighter and more fuel-efficient. Bioplastics can be used in construction to make building products and insulation, which will help the housing industry become more sustainable.
Challenges and Future Directions
Notwithstanding the potential advantages, a number of obstacles need to be overcome in order to fully reap the benefits of turning used oil into bioplastics. The requirement for cutting-edge technology to effectively filter and transform spent oil into premium bioplastics is a major barrier. Existing techniques might be energy-intensive and produce inconsistent results, which could compromise this approach’s overall commercial feasibility.
Consumer acceptability and regulatory norms present another difficulty. For bioplastics made from spent oil to be widely used, they must fulfill performance and safety standards comparable to those of conventional polymers. Furthermore, promoting acceptance and pushing the usage of bioplastics over traditional plastics requires educating people about the advantages and safety of bioplastics.
Research and Innovation
Innovation and continuous research are crucial to overcoming these obstacles. Researchers and engineers are looking at innovative ways to maximize conversion efficiency and reduce energy usage. For instance, improvements in catalyst technology may speed up and increase the yield of chemical reactions that convert spent oil into bioplastics. More advanced purification methods can also guarantee that the final bioplastics are of the highest caliber and leave no toxic residues behind.
In order to further research and provide a framework that will facilitate the commercialization of bioplastics, cooperation between the government, business community, and academia is essential. Promoting a market for these cutting-edge materials would require public awareness campaigns emphasizing the advantages of bioplastics as well as incentives for businesses to invest in sustainable practices.
Benefits of Using Used Oil for Bioplastic Production
- Waste Reduction: Converting used oil into bioplastics helps alleviate the burden of waste disposal associated with used cooking oils and industrial oils.
- Sustainability: Sustainability is promoted via the conversion process, which uses a waste product as a raw material. It lessens the need for fossil fuels, which are normally required for the production of conventional plastic, cutting carbon emissions and assisting in the shift to a circular economy.
- Biodegradability: In comparison to their petroleum-based equivalents, bioplastics made from spent oil can be engineered to break down more quickly in the environment. Because it enables more responsible disposal and lessens the buildup of plastics in landfills and oceans, it is crucial for reducing the long-term effects of plastic pollution.
- Economic Opportunities: The technology and procedures created for turning spent oil into bioplastics have the potential to open up new business opportunities in the waste management and recycling industries. Facilities that specialize in this conversion process can be established to generate employment, boost local economies, and promote innovation in the field of green technology.
Challenges and Considerations
Even with the possible advantages, turning spent oil into bioplastics is not without its difficulties. The technology’s capacity to scale is one major worry. Large-scale used oil volumes can still be efficiently handled by commercial methods, notwithstanding the promising results of laboratory-scale trials.
The safety of the resulting bioplastics for consumer usage also requires the establishment of regulatory frameworks and safety criteria.
Variability in the composition and quality of spent oils is another difficulty because it can impact the homogeneity of the bioplastic that is created. Maintaining production standards and realizing economies of scale require a consistent supply of high-quality feedstock.
Future Directions
More investigation and development will be required to improve the quality of bioplastics made from spent oil and optimize the conversion processes in order to overcome these obstacles. Academic, business, and governmental partnerships can encourage innovation and help develop best practices for the manufacturing of bioplastics.
It’s also essential to invest in the infrastructure needed for gathering and processing used oil. A consistent supply of feedstock for the synthesis of bioplastics can be ensured by community initiatives that promote the collection of spent oil. Increasing public awareness of the value of properly disposing of and recycling spent oils helps strengthen these initiatives and promote a sustainable culture.
Conclusion
One possible way to combat plastic pollution and make efficient use of waste resources is to convert spent oil into bioplastics. Even though there are still obstacles to overcome, the field is fascinating for future study and growth because of its many applications and possible environmental advantages. Bioplastics made from used oil may be a major factor in creating a more sustainable future if industry cooperation and innovation are sustained. We not only lessen environmental problems but also open up new business prospects in the green economy by turning garbage into useful products.